As the real estate landscape continues to evolve, the concept of Rental Income Mortgage (RIM) loan has emerged as a powerful tool, offering a tailored approach to harnessing rental income and expanding eligibility. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of rental income mortgage, shedding light on its significance, application process, and benefits in the realm of using rental income to qualify for a mortgage.
Table of Contents
Understanding Rental Income Mortgage
RIM loans represent a paradigm shift in the mortgage landscape, where rental income is central to determining eligibility. These loans offer a unique opportunity for borrowers to leverage the income generated by their rental properties, allowing them to qualify for a mortgage that might have otherwise been out of reach.
The fundamental principle behind rental income mortgage is simple yet impactful, assessing whether the property’s rental income is sufficient to cover its debt obligations. Unlike traditional mortgages that heavily rely on personal income and credit scores, rental income mortgage prioritizes property’s income-generating capacity as a primary factor in the qualification process.
The Role of Rental Income to Qualify for the Mortgage
Rental income serves as a cornerstone in the qualification process for a RIM loan, enabling borrowers to leverage the property’s income potential to secure financing. This specialized type of mortgage places significant emphasis on the property’s ability to generate rental revenue and cover debt obligations. Here’s how rental income assists borrowers in qualifying for a RIM loan:
1. Income Sustainability
RIM loans recognize the stability and predictability of rental income. Rental properties with a history of consistent cash flow are attractive to lenders, as they provide a reliable source of funds to cover expenses, including the mortgage.
2. Rental Income Mortgage (RIM)
The primary factor that differentiates RIM loans is the focus on RIM. This ratio quantifies the relationship between the property’s net operating income (NOI) and its debt payments. Rental income contributes to the property’s NOI, allowing borrowers to achieve a higher RIM and meet lender requirements.
3. Enhanced Qualification Potential
Rental income can be a strong compensatory factor for borrowers who may not meet traditional income criteria. The ability of rental income to augment the borrower’s overall cash flow enhances the likelihood of meeting the lender’s RIM threshold.
4. Diversification of Income
Rental income diversifies a borrower’s income portfolio, reducing reliance solely on personal earnings. This diversification contributes to a healthier financial profile and demonstrates the borrower’s capacity to manage multiple income streams.
5. Higher Loan Amounts
Rental income’s positive impact on the property’s cash flow can lead to higher loan amounts. A property with strong rental income potential may qualify for a larger loan, allowing borrowers to invest in properties with greater income potential.
6. Flexible Documentation
RIM loan often has more flexible documentation requirements compared to traditional mortgages. The emphasis on rental income provides borrowers with alternative pathways to meet qualification criteria.
In essence, rental income is a powerful tool that empowers borrowers to qualify for a RIM loan by demonstrating the property’s ability to generate consistent income and cover debt obligations. However, understanding related requirements can enhance the chances of loan approval before applying for the RIM loan.
Eligibility Requirements for Rental Income Mortgage
Qualifying for a RIM (Rental Income Mortgage) loan involves meeting specific criteria that focus on the property’s income-generating potential and its ability to cover debt obligations. This loan prioritizes rental income and the property’s financial stability. Here are the key requirements to qualify for a RIM loan:
1. Property Cash Flow
The property’s cash flow, primarily generated from rental income, is a central consideration. The rental income must demonstrate a consistent and sufficient revenue stream to cover the property’s operating expenses, mortgage payments, and other debt obligations.
2. Rental Income Mortgage (RIM)
The property’s RIM must meet or exceed the lender’s specified threshold. Lenders typically require a RIM of at least 1, indicating that the property’s income covers its debt payments comfortably.
3. Borrower’s Creditworthiness
While RIM loans prioritize property performance, the borrower’s creditworthiness is still considered. A satisfactory credit score of 620 or more can contribute to the borrower’s overall eligibility.
4. Down Payment
Some RIM loan programs may require a higher down payment compared to traditional mortgages. The borrower’s ability to provide a substantial down payment demonstrates commitment and financial stability.
5. Property Type
RIM loans are commonly applicable to various types like rental properties, commercial properties, and vacation homes. The property’s type and intended use play a role in determining its eligibility for a RIM loan.
6. Property Condition
Lenders assess the property’s overall condition and market value. A well-maintained property with positive rental history is more likely to meet the lender’s requirements.
7. Reserves
Lenders may require the borrower to have reserves, such as cash or liquid assets, to cover potential vacancies, repairs, or unexpected expenses. Adequate reserves enhance the property’s ability to withstand financial challenges.
8. Property Management Plan
A well-defined property management plan that outlines how the borrower intends to manage and maintain the rental property can contribute to a favorable loan decision. Lenders appreciate a strategic approach to property management.
9. Documentation
Comprehensive documentation of rental income, lease agreements, operating expenses, and other financial information is essential to support the property’s income potential and financial stability.
10. Appraisal
A qualified professional’s appraisal helps assess the property’s value and rental income potential. A well-documented appraisal contributes to accurate calculations of NOI and RIM.
Meeting these requirements demonstrates the property’s income stability, the potential for generating rental revenue, and overall financial viability. As RIM loans focus on property performance, borrowers must present a compelling case that their rental property can effectively cover its financial obligations and provide a consistent income stream.
Applying for a Rental Income Mortgage: Key Steps and Considerations
Applying for a RIM (Rental Income Mortgage) loan involves a strategic process that showcases your property’s income potential to qualify for the mortgage. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you navigate the application process for a RIM loan:
1. Gather Documentation
Collect comprehensive documentation of your property’s rental income, including lease agreements, rental history, and any other relevant income sources.
Compile detailed financial statements that highlight the property’s net operating income (NOI) and operating expenses.
2. Calculate Rental Income Mortgage (RIM)
Determine your property’s NOI by subtracting operating expenses from rental income. Calculate your property’s RIM by dividing NOI by your total debt payments, including the mortgage.
3. Research Lenders
Identify lenders (new link)who offer RIM loans or specialize in rental income-based mortgages. Research their requirements, terms, and eligibility criteria to ensure they align with your financial situation and property. HomeAbroad can help you find the best RIM mortgage lenders, as we have a vast network of promising lenders who have helped many aspiring investors realize their dreams.
4. Provide Documentation
Submit the documentation you’ve gathered to the lender for their review. Include lease agreements, rental income history, property expenses, and any other financial information they require.
5. Undergo Property Evaluation
Lenders may conduct a thorough evaluation of the property’s rental income potential.
An appraiser may assess the property’s value based on its income-generating capacity.
6. RIM Calculation and Analysis
The lender will calculate the RIM based on the provided documentation and property evaluation. They will analyze whether your property meets their required RIM threshold for loan qualification.
7. Negotiate Loan Terms
Discuss loan terms, interest rates, repayment periods, and any other relevant details with the lender. Review the proposed terms to ensure they align with your financial goals.
8. Submit Loan Application
Complete the lender’s loan application process, providing all required personal and financial information.
Include details about your property, rental income, and any other relevant assets.
9. Credit Check and Underwriting
The lender will conduct a credit check and underwriting process to assess your creditworthiness and evaluate the loan’s risk.
10. Loan Approval and Closing
You’ll receive loan approval if your application meets the lender’s criteria. Review and sign the loan agreement and complete any remaining documentation.
Remember using rental income to qualify for the mortgage application process may vary depending on the lender’s specific requirements and the complexity of your property’s income potential. Consulting with a mortgage advisor or financial expert specializing in RIM loans can provide valuable guidance throughout the application process and increase your chances of successfully securing the loan based on your rental income.
Benefits of Rental Income Loan
RIM loans offer several compelling advantages for borrowers seeking to use rental income to qualify for a mortgage:
1. Enhanced Eligibility
RIM loans expand eligibility by leveraging rental income, allowing borrowers with strong property cash flow to qualify for larger loan amounts.
2. Investment Growth
RIM loans empower real estate investors to capitalize on their rental properties’ income potential, supporting portfolio growth and wealth accumulation.
3. Flexible Criteria
By prioritizing property income, RIM loans provide flexibility for unconventional borrowers, including self-employed individuals or those with limited credit history.
Rental Income Mortgage vs. Traditional Mortgage: A Comparative Overview
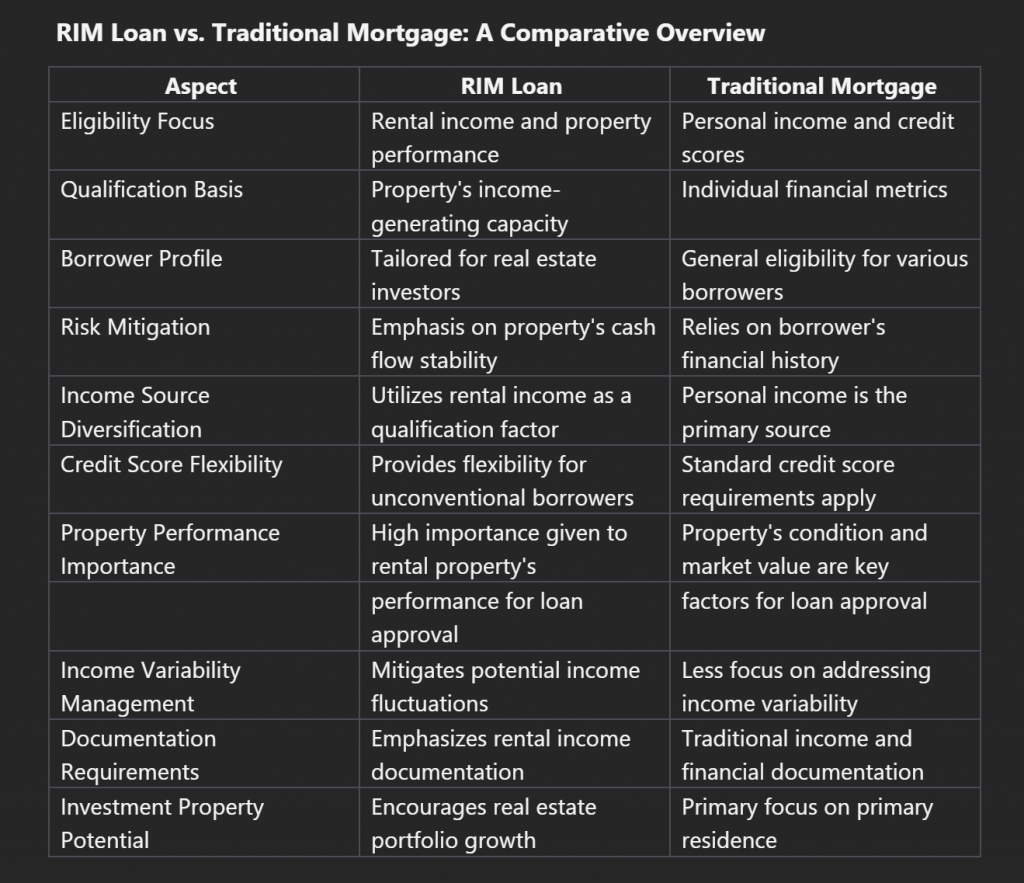
Source: HomeAbroad
How Much Rent is Tax-Free? Considerations for Borrowers
A common inquiry for individuals considering rental income as a mortgage qualification factor is: “How much rent is tax-free?” The tax implications of rental income can vary based on factors such as property type, location, and local tax laws. Consulting with a tax professional can provide insights into the potential tax benefits and obligations related to rental income.
Conclusion: Empowering Homebuyers Through RIM Loans
RIM loans represent a game-changing approach to mortgage qualification, empowering borrowers to harness the income potential of their rental properties. By using projected income to qualify for a mortgage, RIM loans offer a pathway to homeownership that aligns with the evolving dynamics of the real estate market. As you embark on your homeownership journey, consider the transformative possibilities that RIM loans can offer, unlocking the doors to your dream home through the power of rental income.
HomeAbroad specializes in DSCR loans, offering the most competitive terms and swift approvals. Get your rate quote today!

Pre-qualify for a DSCR Loan in a Few Clicks.
No Paystubs, W2s, or Tax Returns Required.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. How do you prove rental income for a loan?
To verify your rental income, lenders will typically request:
Your most recent tax return
A profit and loss statement (if you’re self-employed)
Bank statements from the past few months
A signed copy of your lease agreement
Q2. Does a rental property count against your debt-to-income ratio?
Once you own the home, the debt will be considered. If you are renting or intend to purchase and stay where you live, your rental cost will be included. Your projected housing expenses include the principals, interest, taxes, insurance, and the HOA fees.
Q3. How is rental income taxed?
Rental income is subject to the same tax rules as any other income you earn. You must report your rental profit or loss on your annual tax return. However, you may be able to deduct certain expenses, like repairs, maintenance, mortgage interest, and property taxes.
Q4. What is a good net yield on a rental property?
There is no definitive answer, as a good net yield depends on your circumstances. However, many landlords aim for a 5-10% net yield. This means that, after deducting all running costs and mortgage payments, they’re left with a profit of 5-10% of the property’s value each year.
Q5. What is future rental income?
The amount you anticipate making from renting and residing in them is your future rental earnings. When determining your loan eligibility, we use this term from the mortgage industry, which refers to projected rental income. All types of properties fall under these terms. However, your rental income may help with the additional payment for your new mortgage, or it may help. Most people cannot obtain a mortgage without additional funds from tenants.
Q6. Do I need to find a tenant and have a written lease agreement for my rental property before I apply for a mortgage?
Lenders will require either a fully executed lease agreement or a rental history for the past 12 months. If you do not have a tenant, you may use a family member or yourself as a placeholder until you find a paying tenant.
Qualifying for a mortgage can be tedious, especially if you’re self-employed or have rental income. However, there are a few ways that you can use rental income to qualify for a mortgage. You can either use 75% of your total rental income (after deducting costs) to increase your income, or you can use Form 1037, 1038, or 1039 from Fannie Mae to calculate your potential rental income. If you have any questions, be sure to ask your lender or a housing counselor.
Q7. When is predicted rental income accepted for underwriting?
Because rental income is seldom proven in tax returns, if you recently bought a home, your rental income would be estimated and could possibly be used in other areas. Showing the property’s earning potential is another way to go about this. If the renters have tenants, then the lender may use a percentage of their earnings as an estimate for the renter’s income.
Q8. Does rent count as income for a mortgage?
Yes, rental income can count as income for mortgage qualification, especially when applying for certain types of mortgages that consider rental income as part of your overall financial picture. This is particularly relevant for investment properties or properties with rental units.
Q9. What are the worksheets required for calculating rental income?
Before submitting your paperwork to a lender, you can use the worksheets provided by Fannie Mae to get an idea of your potential rental income. Depending on how many rental units you have and whether your property is your primary residence, an investment, or a commercial holding, you will need to use one of the worksheets below:
For primary residents with two to four units, use Form 1037
For investment properties, use Form 1038 (up to four properties)
For investment properties, use Form 1038A (up to 10 properties)
Form 1039: For rental income from investment properties for business purposes
Q 10. How Are Leases And Appraisals Used To Determine Rental Income?
The lender will use a portion of the projected income in their calculations for leases and appraisals. They typically use 75% of it, leaving 25% for anticipated vacancies.
Q11. What Impact Does Rental Income Have On Your Net Cash Flow?
The lender will also consider your net cash flow if you have rental properties. In the majority of financial scenarios, net cash flow is calculated by deducting expenses from income. However, things get a little trickier when renting a place. Lenders once more use 75% of your total rental income, in this case, before deducting costs.
You’re in luck if the outcome is a positive number. Your income is then increased by that sum. If not, though, it will be considered a loss, so you’ll have to find a way to make up for it somewhere else.







![DSCR Loan Interest Rates Today [July, 2025]](https://homeabroadinc.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/DSCRLoanInterestRates.jpg)
![How to Get DSCR Loans for Airbnb? [A 2025 GUIDE]](https://homeabroadinc.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/DSCR-loans-for-airbnb.png)













